Embedded Workflow#
On this page, we provide documentation of workflows to deploy acados on different embedded systems.
We want to encourage you to contribute a description of the workflow to deploy acados on an embedded system that is not yet mentioned on this page by creating a pull request.
dSPACE DS1202#
Here, the workflow for the deployment of acados on a dSPACE RCP Platform is described.
This has been successfully tested for the DS1202 MicroLabBox.
NOTE: It has also been tested for the DS1401 MicroAutoBox-II (MABX2).
In the following DS1202 should always be replaced with DS1401 for the MABX2 workflow.
In the next section another workflow for DS1401 and DS1403 is also explained.
Prerequisites#
you were able to install
acadosand dSPACE on your systemyou were able to generate S-Functions with acados, which also work in your Simulink simulation
'Simulation_Model_Name'.slx. Thus, you have a folderc_generated_codewith your S-Functions, amake_sfun.mMATLAB script (and amake_sfun_sim.mscript, if needed) and the corresponding C files.you have prepared a Simulink model with the name
'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slx, which does not contain the S-Functions yet and you were able to compile it for your dSPACE Platform. During the compilation process, the dSPACE Makefile'dSPACE_Model_Name'_usr.mkwas created, which can be found in the same directory as the dSPACE Simulink model.
Step 1: Adapt the existing CMake toolchain file for your system#
The CMake toolchain file, needed to cross-compile acados for the dSPACE Platform contains paths to compilers, provided in the dSPACE installation.
As the dSPACE installation varies from system to system, this toolchain file first has to be adapted.
The Toolchain files are located in
'acados_root_folder'/cmake. The toolchain file for the MicroLabBox is calledToolchain-dSpaceDS1202.cmakeand can be edited with any editor (respectivelyToolchain-dSpaceDS1401.cmakefor the MicroAutoBox-II).The lines that contain the paths to the compilers have to be adapted to fit your system. Specifically, the folder name which consists of a long number (here: 1184D92C-D928-4591-A1E9-B54339797C20) varies. For example for
DS1202: On your system inC:/ProgramData/dSPACE/, find the folder which contains the directories/Compiler/QNX650_520/host/win32/x86/and/Compiler/QNX650_520/target/qnx6/, and update the two paths in the toolchain file.
Define environment variables used within the toolchain file, currently only required for DS1202:
Define an environment variable (type
envin the windows search bar and openEdit the windows environment variables. There, clickEnvironment Variables...and create a new entry for your user) with the nameQNX_HOSTand as the value, enter the path you set before in the toolchain file.Define an environment variable with the name
QNX_TARGETand as the value, enter the path you set before in the toolchain file.
Step 2: Cross-compile acados for your dSPACE platform#
In order to compile acados for your dSPACE platform, you need the acados libraries and header files in the correct format.
These files can be created by cross-compiling the acados source code for the correponding dSPACE platform.
Using a toolchain CMake file, the following steps are needed in order to create the necessary files:
Similar to the
acadosinstallation process, create a new folderbuildDS1202in theacadosroot folder.In your powershell, navigate to this folder and then run:
cmake -D CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../cmake/Toolchain-dSPACEDS1202.cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -S ../ -B ./In order to cross-compile acados, run:
cmake --build ./In order to install the cross-compiled
acadosversion, run:cmake --install ./If all these steps worked, you will find the two folderslibandincludeinbuildDS1202/install. These are the folders you need to deployacadoson your dSPACE Platform.
Step 3: Create a dSPACE build folder, prepare Simulink model#
Create a new folder
'dSPACE_Build_Folder_Name'(anywhere) and copy your Simulink model'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slx, the dSPACE Makefile'dSPACE_Model_Name'_usr.mkand theacadosS-Function folderc_generated_codeto this folder.Copy the two folders
libandinclude, which you created in the cross-compiling process (Step 2), to this folder too.Add the folders
c_generated_codeandlibto the MATLAB search path.Open the Simulink model
'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slx, and copy theacadosS-Function(s) from the Simulink simulation file'Simulation_Model_Name'.slxinto the dSPACE Simulink model. Make sure the S-Function(s) get the correct inputs (Ctrl+D to check).
Step 4: Adapt the dSPACE Makefile#
Adapt the dSPACE Makefile in order to include the acados headers, libraries and additional C code source files.
Your
acadosS-Function(s) are based on C code source files. These files are listed asSOURCESin the MATLAB scriptmake_sfun.m(andmake_sfun_sim.mif the simulation S-Function is used too). Open the dSPACE Makefile'dSPACE_Model_Name'_usr.mkand list all source files needed for the S-Functions, except for the ones which have the same name as the S-Functions.Example:
If the sources listed in
make_sfun.m(solver S-Function name: acados_solver_sfunction_OCPModelName) read as:SOURCES = [ ... 'OCPModelName_model/OCPModelName_expl_ode_fun.c ', ... 'OCPModelName_model/OCPModelName_expl_vde_forw.c ',... 'acados_solver_sfunction_OCPModelName.c ', ... 'acados_solver_OCPModelName.c ' ];
and the Sources listed in
make_sfun_sim.m(sim S-Function name: acados_sim_solver_sfunction_OCPModelName) are:SOURCES = [ 'acados_sim_solver_sfunction_OCPModelName.c ', ... 'acados_sim_solver_OCPModelName.c ', ... 'OCPModelName_model/OCPModelName_expl_ode_fun.c ', ... 'OCPModelName_model/OCPModelName_expl_vde_forw.c ',... ];
The entry in the dSPACE Makefile should read as:
# Additional C source files to be compiled (file name extension .c). USER_SRCS = \ OCPModelName_expl_ode_fun.c \ OCPModelName_expl_vde_forw.c \ acados_solver_OCPModelName.c \ acados_sim_solver_OCPModelName.c
Define the (relative) paths to the S-Functions and the C code source files in the dSPACE Makefile. These are the folder
c_generated_codeand any subfolder which contains C code source files, which were identified in the previous step. For the example in the previous step the entry in the dSPACE Makefile would look like this:# Directories where S-Function C source files are stored. SFCN_DIR = \ "\c_generated_code" \ "\c_generated_code\OCPModelName_model"
Define the (relative) paths to the
acadosheader files in the dSPACE Makefile. With hpipm as a solver, this looks as follows:# Path names for user include files. USER_INCLUDES_PATH = \ "include" \ "include\blasfeo\include" \ "include\hpipm\include"
Define the libraries needed to compile the S-Functions. With hpipm as a solver, this looks as follows:
# Additional user libraries to be linked. # NOTE: these might be *.lib for other systems USER_LIBS = \ lib\libblasfeo.a \ lib\libhpipm.a \ lib\libacados.a
Save the dSPACE Makefile.
Step 5: Compile your dSPACE Simulink model for dSPACE#
In order to compile your dSPACE Simulink model 'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slx use the rtwbuild command in MATLAB or press Ctrl+B in Simulink.
The Makefile should now integrate all the necessary files for the compilation of the acados S-Functions.
dSPACE DS1401 and DS1403#
Here, an alternative workflow for the deployment of acados on a dSPACE Platform is described.
This has been successfully tested with MATLAB / Simulink R2018b on the DS1401 MicroAutobox-II (MABX2) and the DS1403 MicroAutobox-III (MABX3).
With some adaptation this method could also work with different dSPACE Platforms.
Prerequisites#
you were able to install
acadosand dSPACE on your systemyou were able to generate S-Functions with acados, which also work in your Simulink simulation
'Simulation_Model_Name'.slx. Thus, you have a folderc_generated_codewith your S-Functions, amake_sfun.mMATLAB script (and amake_sfun_sim.mscript, if needed) and the corresponding C files.you have prepared a Simulink model with the name
'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slx, which does not contain the S-Functions yet and you were able to compile it for your dSPACE Platform.your dSPACE installation, and your project folder, do not contain spaces in their paths (all the paths you will use in the next steps should not contain any space). It is usually sufficient to copy-paste the compiler folder to a new one without spaces in it, without re-installing the whole dSPACE software suite)
Step 1: Adapt the CMake toolchain file for your system#
The CMake toolchain file, needed to cross-compile acados for the dSPACE Platform contains paths to compilers, provided in the dSPACE installation.
As the dSPACE installation varies from system to system, this toolchain file first has to be adapted.
The toolchain files are located in
'acados_root_folder'/cmake.The toolchain file for MABX2 is called
Toolchain-dSpaceDS1401.cmake, the one for MABX3 is calledToolchain-dSpaceDS1403.cmake.The lines that contain the paths (line 1 - 17) to the compilers have to be adapted to fit your system. It is possible to locate the correct compiler path from the Simulink dSPACE build output (e.g. building
'dSPACE_Model_Name'.slxwithout acados S-Functions in it):
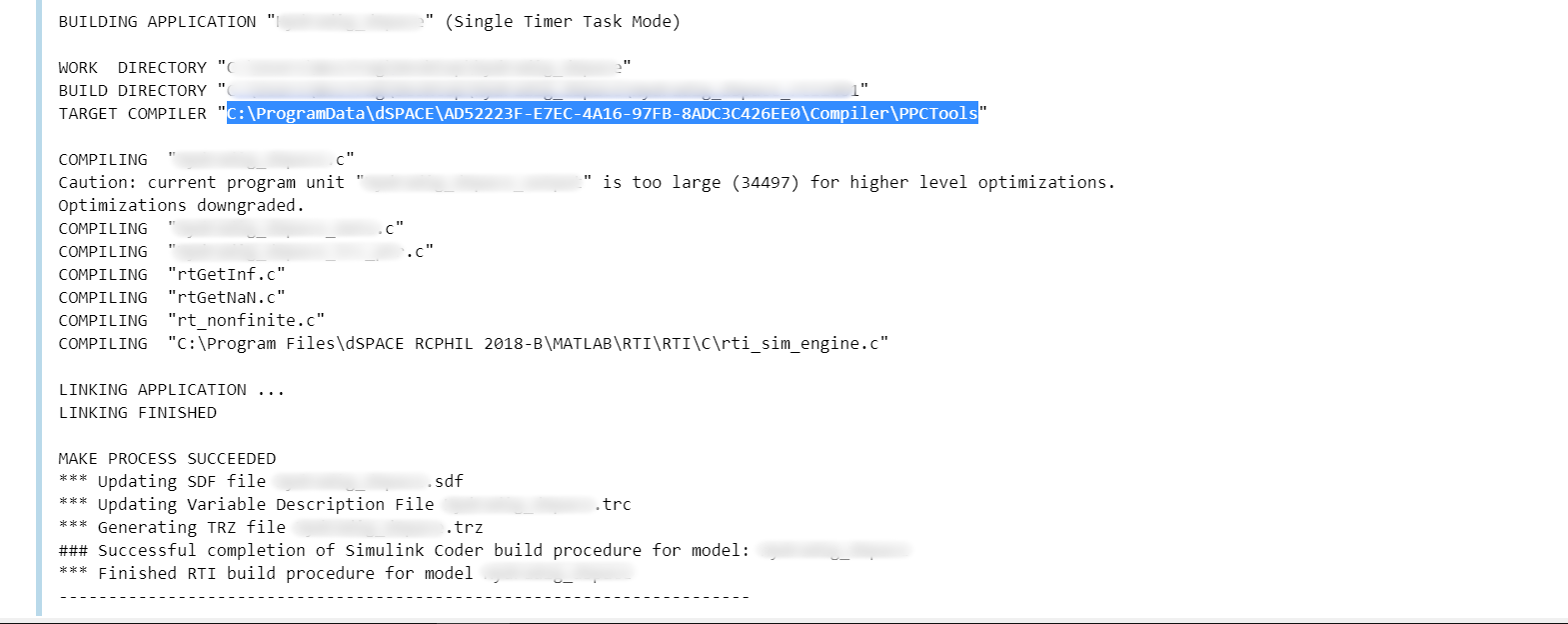
Step 2: Cross-compile acados for your dSPACE platform#
In order to compile acados for your dSPACE platform, you need the acados libraries and header files in the correct format.
These files can be created by cross-compiling the acados source code for the correponding dSPACE platform.
Using a toolchain CMake file, the following steps are needed in order to create the necessary files:
Similar to the
acadosinstallation process, create a new folderbuildDS1401(orbuildDS1403) in theacadosroot folder.In your powershell, navigate to this folder and then run:
cmake -D CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../cmake/Toolchain-dSPACEDS1401.cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -S ../ -B ./Be sure to use the correct*.cmakefile.In order to cross-compile acados, run:
cmake --build ./In order to install the cross-compiled
acadosversion, run:cmake --install ./If all these steps worked, you will find the two folderslibandincludeinbuildDS401/install(orbuildDS1403/install). These are the folders you need to deployacadoson your dSPACE Platform.
Step 3: Prepare and build Simulink model#
Add
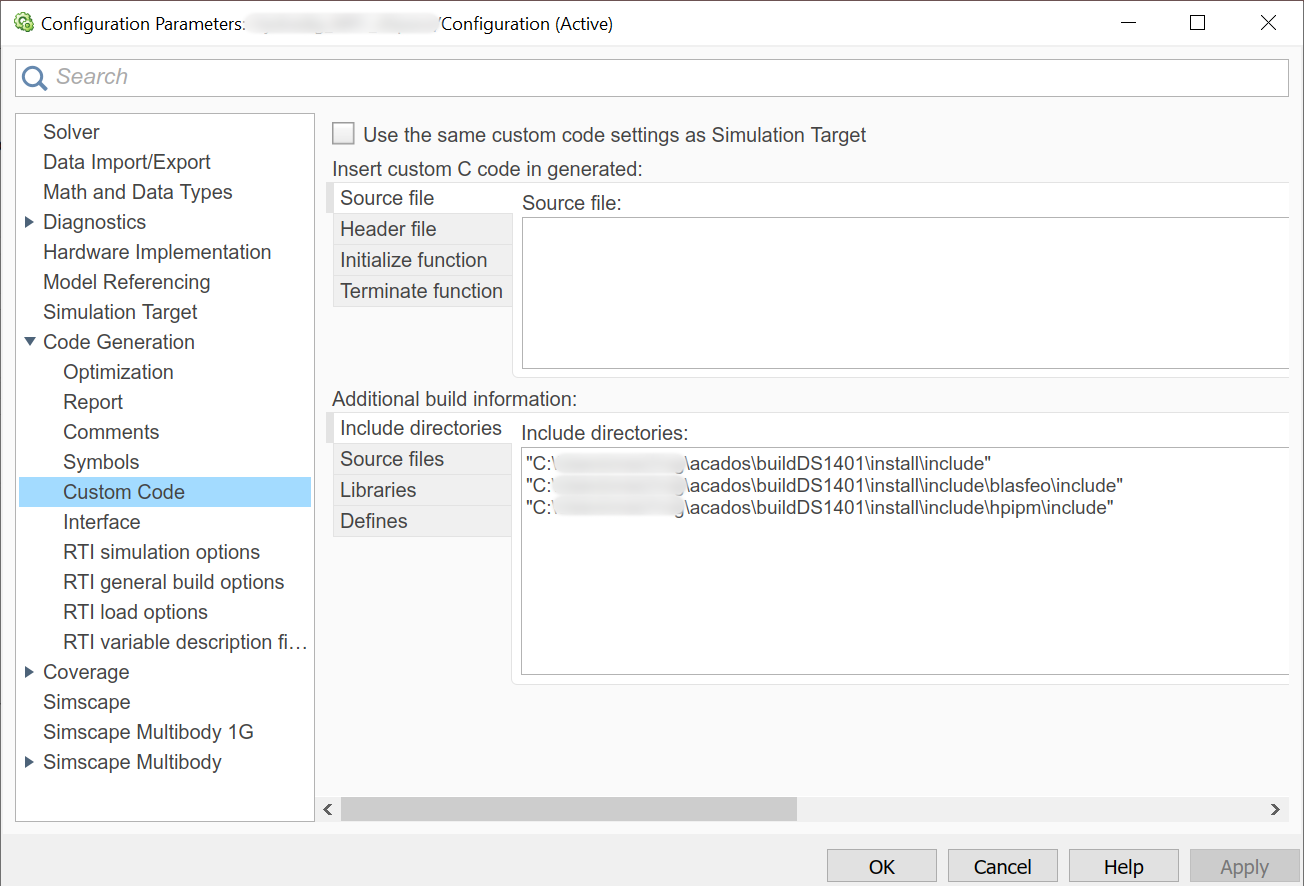
c_generated_codefolder to MATLAB path.Open Simulink model configuration parameters, and under Code Generation / Custom Code / Additional build info, add the following paths:
Include directories: all the include directories in the
buildDS1401/install/include(orbuildDS1403/install/include) folder as in this example:
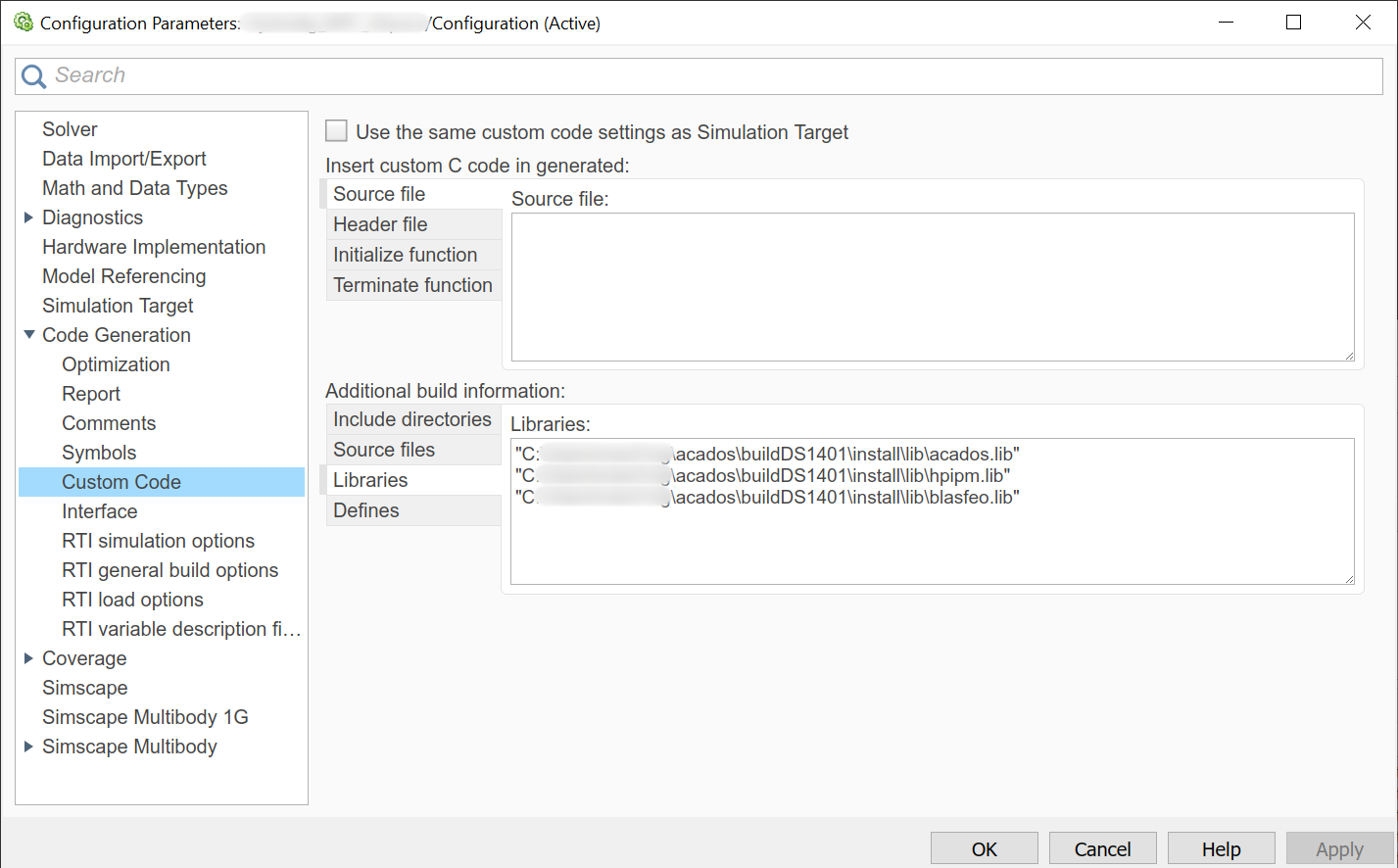
Libraries: all acados
*.libfiles in thebuildDS1401/install/lib(orbuildDS1403/install/lib) folder as in this example:
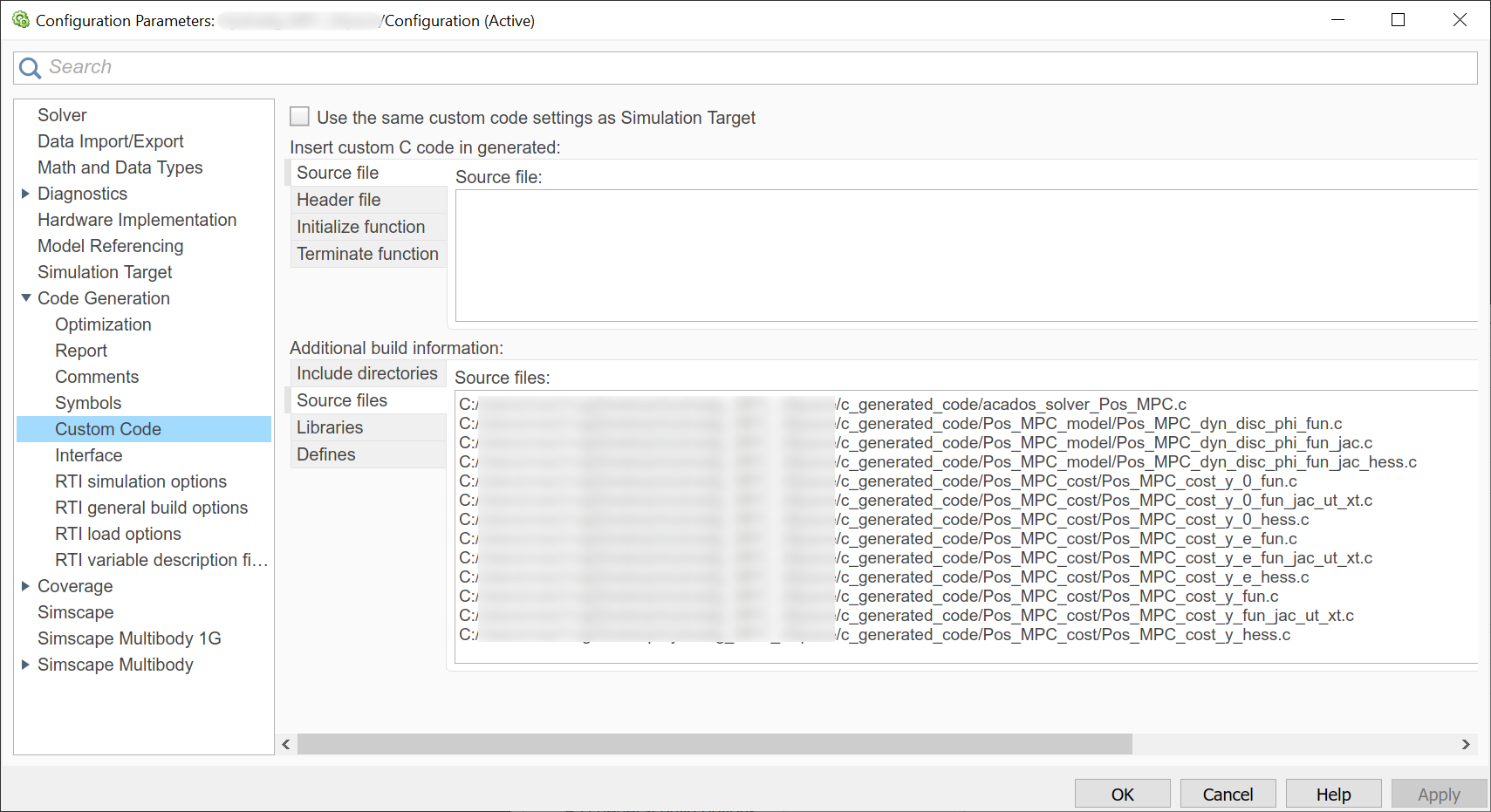
Source files: all
*.cfiles in yourc_generated_codefolder, as in the example below Note that these files may change based on the selectedacadosocp options. It is possible to obtain a space separated list of all the*.cfiles by running the following command in thec_generated_codefolder:find "$(pwd)" -type f -not -path "*examples*" -name "*.c" | tr '\n' ' ' | sed 's/\/c\//C:\//g'
Build the dSPACE Simulink model as usual, pressing Ctrl+B in Simulink.
